Automatic Transfer Switches
Share
Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS): A Complete Guide for Reliable Power Backup
When the power goes out, businesses and homeowners rely on backup generators to keep the lights on and critical systems running. But what ensures that the transition between utility power and backup power happens seamlessly? The answer: an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS).
In this article, we’ll explain what an ATS is, how it works, why it’s essential, and what to consider when choosing the right transfer switch for your needs.
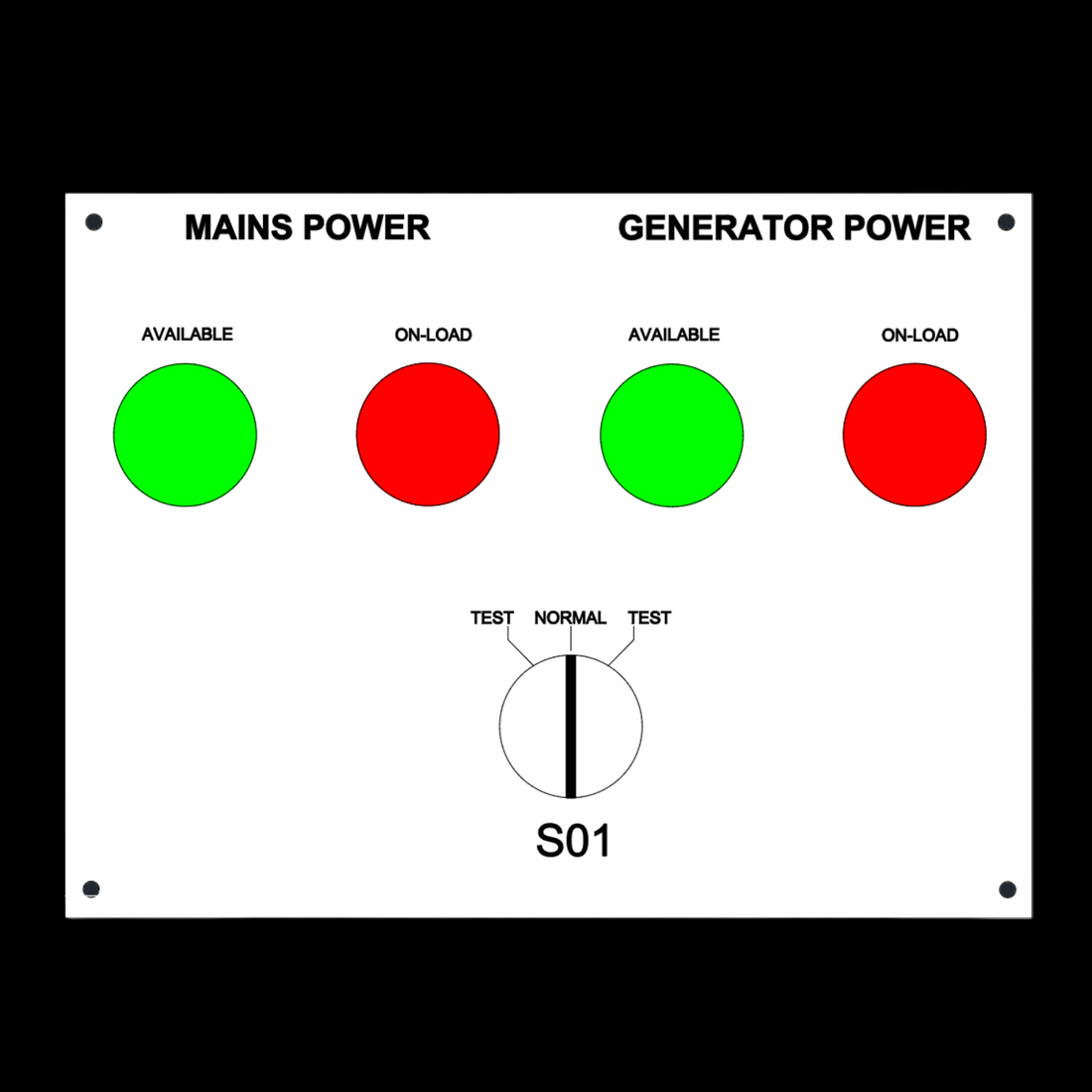
What is an Automatic Transfer Switch?
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is an electrical device that automatically detects a power outage and transfers the load from the utility source to a backup generator or alternative power source. Once utility power is restored, the ATS switches back to the main supply without manual intervention.
Think of it as the “traffic controller” for your electrical system—ensuring continuous power supply, safety, and efficiency.
How Does an ATS Work?
The operation of an automatic transfer switch involves three key steps:
- Power Monitoring – The ATS constantly monitors the main utility power.
- Detection & Transfer – When it senses a power failure or voltage irregularity, it sends a signal to start the generator and transfers the load automatically.
- Re-Transfer to Utility – Once stable power returns, the ATS safely switches back to the utility and shuts down the generator.
This process happens in seconds, minimizing downtime and protecting sensitive equipment.
Benefits of an Automatic Transfer Switch
Investing in an ATS offers multiple advantages:
- Uninterrupted Power Supply – Keeps essential systems like HVAC, security, medical equipment, and servers running.
- Safety & Reliability – Prevents dangerous back-feeding into the utility line and ensures smooth transitions.
- Convenience – Eliminates the need for manual switching during outages.
- Equipment Protection – Stabilizes voltage transfer, reducing wear and tear on electronics and appliances.
Types of Automatic Transfer Switches
There are several types of ATS solutions, designed for different applications:
- Open Transition ATS (Break-Before-Make) – Safely disconnects from one source before connecting to another.
- Closed Transition ATS (Make-Before-Break) – Provides seamless transfer with no power interruption.
- Soft Load ATS – Balances load between utility and generator, reducing stress on equipment.
- Bypass Isolation ATS – Ideal for critical facilities, allowing maintenance without interrupting power.
Applications of ATS
Automatic transfer switches are widely used across industries and residential settings, including:
- Hospitals & Healthcare Facilities – Ensuring life-saving equipment never loses power.
- Data Centers – Protecting servers and preventing costly downtime.
- Industrial Plants – Maintaining production processes.
- Commercial Buildings – Keeping businesses operational during outages.
- Residential Homes – Providing peace of mind during storms and blackouts.
Choosing the Right ATS
When selecting an automatic transfer switch, consider:
- Load Size & Capacity – Match the ATS to your generator and total load demand.
- Switching Type – Open vs. closed transition, depending on application needs.
- Compliance & Safety Standards – Look for UL-listed and NEC-compliant equipment.
- Professional Installation – Always consult a licensed electrician to ensure proper setup.
Final Thoughts
An Automatic Transfer Switch is the backbone of any reliable backup power system. Whether for a hospital, business, or home, an ATS ensures a safe, efficient, and automatic transition between power sources—keeping you protected from costly outages and disruptions.
If you’re considering installing an ATS, consult with a certified electrician or power solutions provider to find the right model for your needs.
